A cable connector enables the physical connection of two devices for various uses. These include connecting hardware devices to a system using a PC cable, connecting to a network using a networking cable, and connecting audio and video equipment to a system using an audio/video cable. Read More…
Aries Electronics Inc. manufactures electronic interconnect products and other electronic components. Some products include zero insertion force test sockets, intelligent connectors, adapters, ball grid array sockets, land grid array sockets, high-frequency test sockets, and burn-in sockets.
Interpower is a company that is committed to providing industries with high-quality products. We manufacture electronic connectors. We make it easy for customers to design, build and maintain products for worldwide markets. We use teamwork to provide fast turnaround and great service to our customers.
Quail Electronics is a leading supplier of electrical components such as power cords and appliance electronic connectors. If you don't find what you need in our stock items, we can customize a product to meet needs.

Kord King manufactures world class electronic connectors, electric cords and plugs, electrical receptacles, plug adapters, cord sets and much more. From initial design to development, whether you are looking for a cable assembly or a power supply cord, the experienced team at Kord King delivers rapid order turn-around times and excellent products – consistently adhering to our strict quality...

More Cable Connector Manufacturers
Cable Connector Terminology
Understanding cable connector terminology is crucial for engineers, IT professionals, purchasing managers, and anyone researching electronic connectors for consumer or industrial applications. Familiarity with these key terms will help you make informed decisions while selecting, installing, or troubleshooting cable connectors across a range of devices and industries. Below, we break down the essential vocabulary you’ll encounter when evaluating cable connectors for your project or product line.
Gender
A female connector has a hole in it to receive and hold the pin connectors of an accompanying male connector unit. In electronic and electrical applications, understanding connector gender is fundamental—incorrect mating can result in poor connections, equipment damage, or safety hazards. Determining the right gender is especially important for custom cable assemblies and OEM component sourcing.
Polarity
The orientation of the connector's connection is referred to as polarity. Most connectors only connect in one direction to avoid attaching a connector incorrectly. These connectors are referred to as being keyed or polarized connectors. Proper polarity ensures safe and reliable operation—especially invaluable in power delivery, data transfer, and sensitive signal applications.
Contacts
Contacts are the metal components that provide an electrical connection inside the connector. These conductive parts make a connector function; if they become oxidized or dirty, connectors may not function properly. Contact materials (such as gold-plated, tin, or silver contacts) impact conductivity, corrosion resistance, and long-term performance. High-quality contacts are essential in high-frequency, high-speed, or high-power cable connectors.
Pitch
Several contacts are organized in a repeating pattern on some connectors. Pitch refers to the separation between the centers of the previous and subsequent contacts. Selecting the correct pitch size is necessary for locating compatible matching connectors and designing printed circuit boards (PCBs) or custom cable assemblies.
Mating Cycles
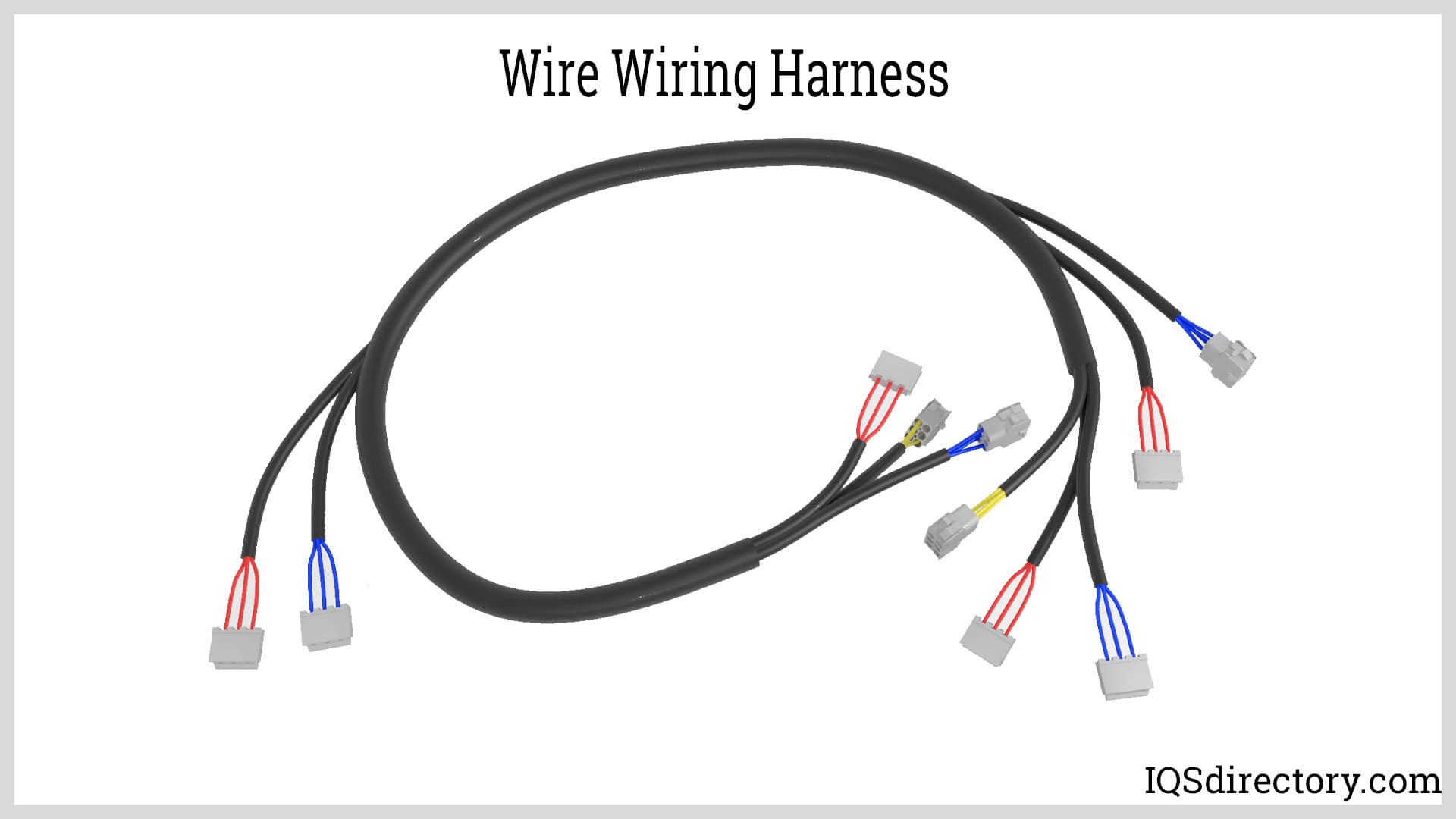
A connector gets worn out over time by being connected and disconnected—a process referred to as mating cycles. A connector is only connected and disconnected once throughout a mating cycle. Connectors can vary widely in the number of mating cycles they support. For instance, board-to-board connectors in consumer electronics may have a maximum mating cycle limit of 10-15, but USB cables can have mating cycles of up to tens of thousands. When choosing connectors for mission-critical or high-usage environments, always review the rated mating cycles for optimal durability and reliability.

Connectors for Device Cables
Device cables use a wide array of connector types, each designed for specific data, power, or signal transmission needs. Understanding the types of connectors used in device cables—ranging from legacy connectors to modern high-speed options—helps you choose the right solution for your application. Below are some of the most common and important device cable connectors you’ll encounter:
Parallel Connectors
Computers once used parallel connectors to link to printers and other peripherals. These now-obsolete wires were fairly robust cables, capable of transferring multiple bits of data simultaneously. However, advancements in speed and miniaturization have rendered parallel connectors largely obsolete in favor of more efficient standards.
Serial Connectors
Serial connectors resemble parallel connectors but were the forerunners of modern USB cables. They fed information sequentially, one bit at a time, and were commonly found in older computer systems and industrial equipment. Despite being largely replaced by USB and Ethernet, serial ports (like RS-232, RS-485) are still valued in automation, data logging, and legacy system integration.
Universal Serial Bus (USB) Connectors
Today, USB connectors are the industry standard for connecting peripheral devices, charging electronics, and enabling data transfer. USB cables come in various types and generations, each with specific data transfer rates, power delivery capabilities, and physical formats. Selecting the right USB connector type is essential for compatibility, performance, and future-proofing your devices. Below are the main USB connector types you’ll encounter:
USB Connectors: Types and Applications
There are three main USB cable versions—1.0, 2.0, and 3.0. Each number represents an improved level of signaling standards through a cable that supports a higher data transfer rate with each subsequent generation. Newer versions such as USB 3.1, USB 3.2, and USB4 further enhance speed, power delivery, and functionality. When comparing USB connectors, consider not just the connector shape but also the supported protocol and data rate.
- USB 1.0/1.1: Up to 12 Mbps, primarily for keyboards, mice, and legacy peripherals.
- USB 2.0: Up to 480 Mbps, widely used for storage devices, printers, and consumer electronics.
- USB 3.0/3.1 Gen 1: Up to 5 Gbps, designed for high-speed data transfer, external hard drives, and advanced peripherals.
- USB 3.1 Gen 2/3.2: Up to 10 or 20 Gbps, supports rapid data transfer and delivers more power for faster device charging.
- USB4: Up to 40 Gbps, supports Thunderbolt 3 compatibility, and is designed for next-generation devices requiring ultra-fast connectivity.

The USB Type-A
USB Type-A connectors are the most recognized and common USB connectors. Universal Type-A connectors feature a rectangular shape and are typically found on host devices such as computers, TVs, and gaming consoles. USB Type-A is widely used for connecting peripherals, flash drives, keyboards, and other accessories. Type-A ports are backward compatible with earlier USB standards, making them a versatile choice for a wide range of device connectivity needs.
USB Type-B
Type-B connectors feature a square plug-in shape and were designed to connect devices like printers, scanners, and certain external hard drives. Type-B connectors offered faster speeds than Type-A connectors and were designed so that users couldn't accidentally connect two computers or misconnect devices. Due to their larger size, Type-B connectors have largely been replaced by more compact connectors, but they are still found in some industrial and commercial equipment. Industries such as manufacturing and laboratory automation rely on robust USB Type-B connections for reliable peripheral integration.
Mini and Micro Type-B USB Cables
Mini-USB and Micro-USB connectors are smaller versions of the standard USB connectors, designed specifically for portable devices. These cables can be used with various mobile devices, including tablets, smartphones, digital cameras, and handheld gaming consoles. Micro-USB, once the industry standard for Android devices, supports both data transfer and device charging. When evaluating connection options for portable and embedded devices, consider the durability and widespread compatibility of mini and micro USB connectors.
USB Type-C Cables
USB Type-C connectors represent the latest evolution in USB technology. These cables can be used with mobile devices and are reversible—meaning devices or connectors can be used in any direction to plug them in. USB-C supports high-speed data transfer, fast charging, video output (DisplayPort, HDMI, Thunderbolt 3), and is rapidly becoming the universal standard across smartphones, laptops, and emerging electronics. For future-proof system designs, choosing USB Type-C connectors ensures broad compatibility and advanced capabilities.
- Are you searching for USB-C cable suppliers or trying to compare USB connector types for your next device launch?
- Want to learn more about USB 3.2 vs USB 2.0 performance for high-speed data transfer?
- Curious about USB-C power delivery features for fast-charging applications?
Explore our comprehensive directory of cable connector manufacturers to find the right supplier for your USB and device cable needs.
Connectors for Audio Cables
Audio cables use a variety of specialized connectors to transmit analog and digital signals between devices. Selecting the best audio connector type depends on your equipment, audio quality requirements, and intended application—from home entertainment systems to professional audio installations and industrial PA systems. Below are the most common audio cable connectors and their typical use cases:
3.5mm Audio Jack
The 3.5mm audio jack is the industry standard connector seen on headphones, smartphones, tablets, and many audio playback devices. These connectors are easily recognized by their cylindrical shape and black stripes. A connector is a 3-pole connector (for stereo audio) if it has two black stripes and a 4-pole connector (for audio + microphone) if it has three black stripes. The additional stripe on the 4-pole connector is used for integrated microphones, making them ideal for headsets, mobile devices, and gaming accessories.
Fiber Optic Audio Cable
Fiber optic audio cables (also known as TOSLINK cables) transmit data via light, delivering high-fidelity digital audio without the electromagnetic interference (EMI) that can affect copper cables. These cables have an advantage over copper wires in that they don't produce any noise, giving off a clear sound. Fiber optic cables are ideal for home theaters, professional audio studios, and high-end AV equipment, where signal clarity and EMI immunity are critical.
Barrel Connectors
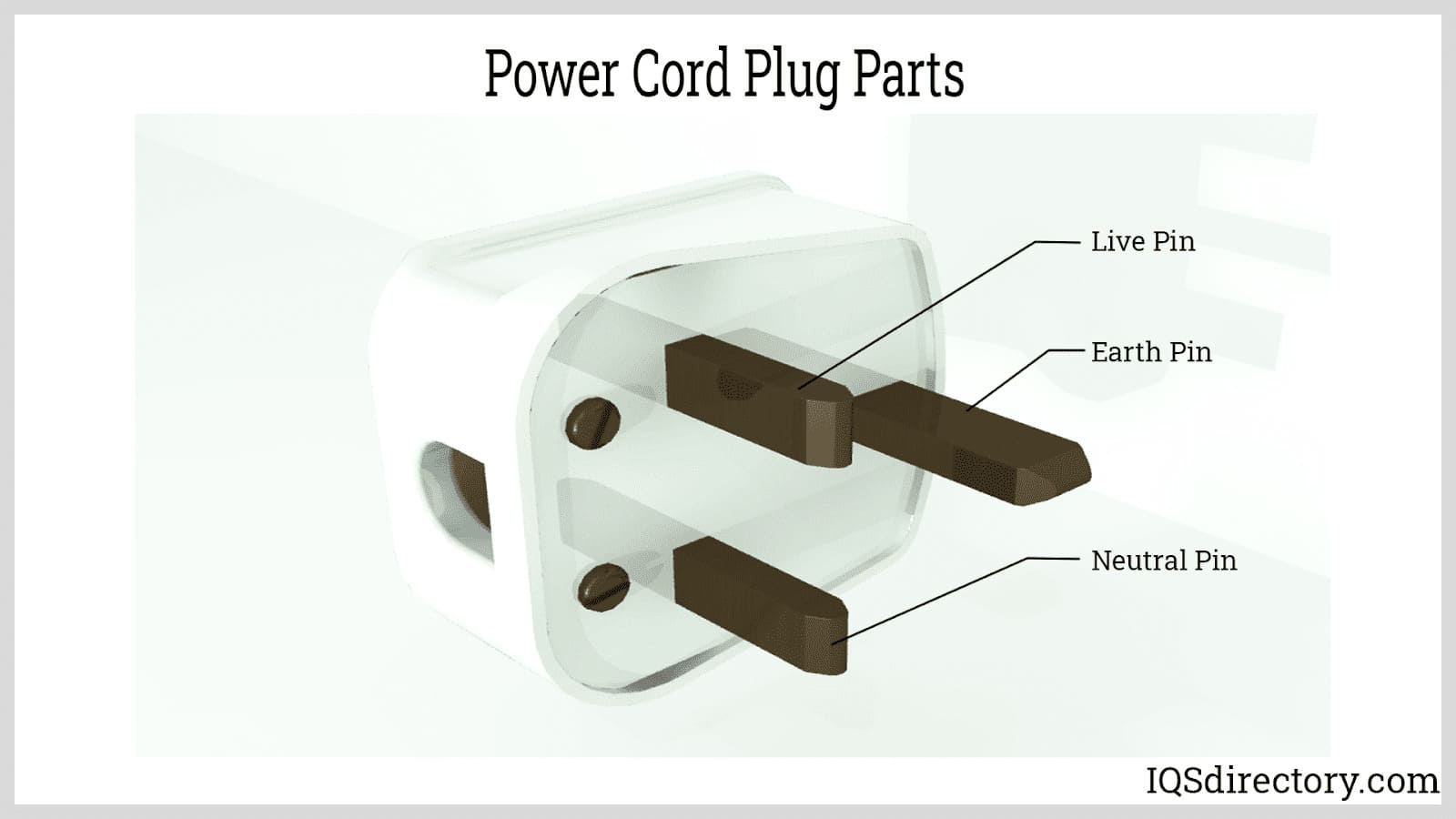
Barrel connectors are cylindrical power connectors commonly used in consumer electronics, such as routers, modems, and small appliances, to connect devices to AC (alternating current) wall adapters. Barrel connections are frequently used to connect electricity to small devices since wall adaptors come in various power and voltage levels. When selecting a barrel connector, always check the diameter, polarity, and voltage specifications to ensure compatibility and safe operation.
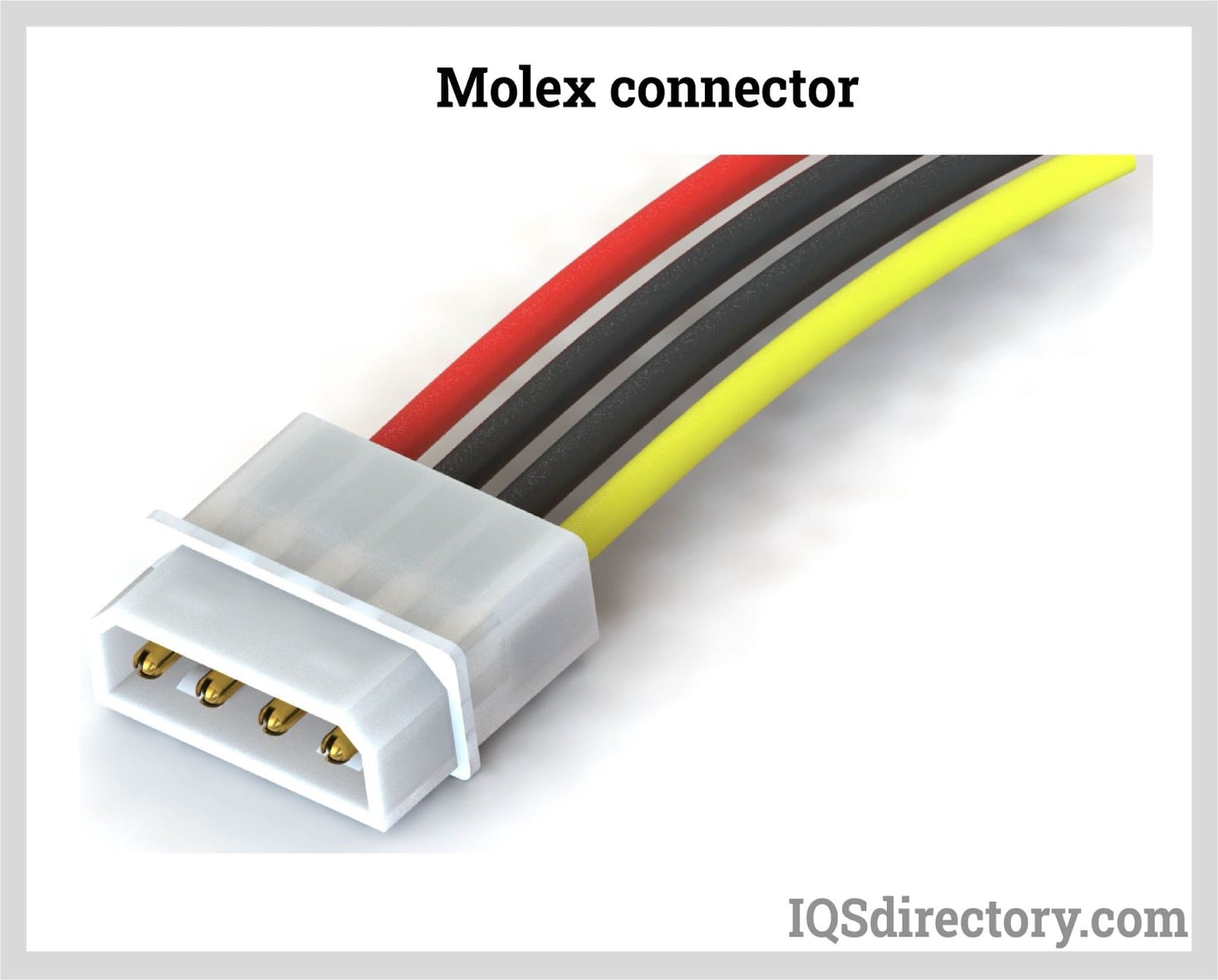
Molex Connectors
Molex connectors are commonly used to supply power to hard drives, optical drives, and other peripheral devices inside computers. These connections have a high current-carrying capacity of up to 11 amps per pin, making them suitable for applications that require a lot of power, like 3D printers, CNC machines, and custom industrial equipment. A female portion of the cable's end fits into a plastic casing that encloses the pins of a male connector. However, these connectors are not appropriate for systems that require frequent connecting and disconnecting because of how tightly they join. For high-power or legacy internal PC components, Molex connectors remain a reliable choice.
- Need help identifying the right audio cable connector for your sound system?
- Looking for a fiber optic audio cable supplier for your home theater or studio?
- Want to compare Molex connectors vs SATA power connectors for PC builds?
Browse our directory of cable connector manufacturers to find audio cable solutions tailored to your technical and performance requirements.
Specialty and Industrial Cable Connectors
Beyond common device and audio cable connectors, the electronics industry relies on a wide array of specialty connectors engineered for demanding industrial, automotive, medical, military, aerospace, and telecommunications applications. These connectors are designed for high reliability, extreme environments, and specialized signal or power requirements. Typical specialty connectors include:
- Coaxial connectors (BNC, SMA, F-type): Used for RF signal transmission in broadcast, CCTV, test equipment, and wireless communication.
- Circular connectors (M12, M8, XLR): Rugged designs for industrial automation, robotics, and professional audio/video systems.
- Rectangular connectors (D-sub, IDC): Used in computing, networking, and industrial control panels for multi-pin connections.
- Waterproof connectors (IP67/IP68 rated): Essential for outdoor, marine, or harsh environment installations, including LED lighting and outdoor electronics.
- Medical-grade connectors: Engineered for patient monitoring, imaging equipment, and surgical devices, meeting strict safety and sterilization standards.
- Automotive connectors (OBD-II, mini-fit): Designed for vehicle diagnostics, infotainment, and power distribution in automotive electronics.
When specifying industrial or specialty connectors, factors such as ingress protection (IP) rating, vibration resistance, ease of termination, and compliance with industry standards (UL, RoHS, REACH) are critical. For harsh environments or mission-critical applications, always partner with a reputable cable connector manufacturer who can provide documentation, testing, and technical support.
How to Choose the Right Cable Connector for Your Application
Selecting the best cable connector for your application involves weighing several technical and operational factors. Making the right choice ensures system reliability, safety, and future scalability. Here are the primary factors to consider when evaluating and purchasing cable connectors:
- Electrical requirements: Voltage, current rating, frequency, and shielding needs.
- Mechanical requirements: Size, durability, mating cycles, and locking mechanisms.
- Environmental factors: Temperature range, ingress protection, chemical exposure, and vibration/shock resistance.
- Compatibility: Pin count, pitch, cable type, and backward compatibility with existing infrastructure.
- Application-specific standards: Industry certifications, fire/safety ratings, and regulatory compliance.
- Ease of installation and maintenance: Tool requirements, field termination options, and serviceability.
- Cost and availability: Price, lead time, and long-term sourcing assurance.
Not sure what type of connector fits your requirements? Ask yourself:
- What operating environment will the connector face (indoor, outdoor, industrial, medical, etc.)?
- What are the electrical and mechanical specifications of your system?
- Which standards or certifications are necessary for your industry?
- Do you need custom cable assemblies or off-the-shelf connectors?
By carefully assessing these decision factors, you can select cable connectors that maximize performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness for your project.
Benefits of High-Quality Cable Connectors
Investing in high-quality cable connectors offers numerous advantages for OEMs, system integrators, and end-users:
- Enhanced reliability: Robust connectors reduce downtime, signal loss, and equipment failure.
- Improved safety: Properly rated connectors mitigate electrical hazards and comply with safety standards.
- Future-proof design: Selecting industry-standard or modular connectors allows for easier upgrades and expansion.
- Reduced maintenance costs: Durable connectors minimize repair and replacement frequency.
- Optimized performance: High-quality connectors ensure superior signal integrity, high data rates, and efficient power delivery.
- Compliance and certification: Certified connectors support regulatory compliance in critical industries such as medical, aerospace, and automotive.
For high-stakes applications, always work with trusted cable connector manufacturers who provide product documentation, quality assurance, and customization options.
Choosing the Right Cable Connector Supplier
To ensure you have the most positive outcome when purchasing cable connectors from a cable connector supplier, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of cable connector suppliers. Each cable connector supplier has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the company for more information or request a quote. Review each cable connector business website using our proprietary website previewer to learn more about what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple cable connector companies with the same form.
When selecting a supplier, consider:
- Product range and specialization: Does the supplier offer the connector types, cable assemblies, or custom solutions you need?
- Quality assurance: Are products tested, certified, and compliant with industry standards?
- Customer support: Does the supplier offer technical assistance, documentation, and post-sales support?
- Lead time and logistics: Are products available when you need them, and can the supplier accommodate your production timeline?
- Pricing and value-added services: Does the supplier offer competitive pricing, prototyping, or design assistance?
Ready to request a quote for cable connectors or find custom cable assembly manufacturers? Use our RFQ form to get fast, accurate responses from leading cable connector suppliers.
For additional resources, technical guides, and expert advice on choosing cable connectors, visit our comprehensive resource center or connect with our network of industry-leading cable connector manufacturers.









 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services