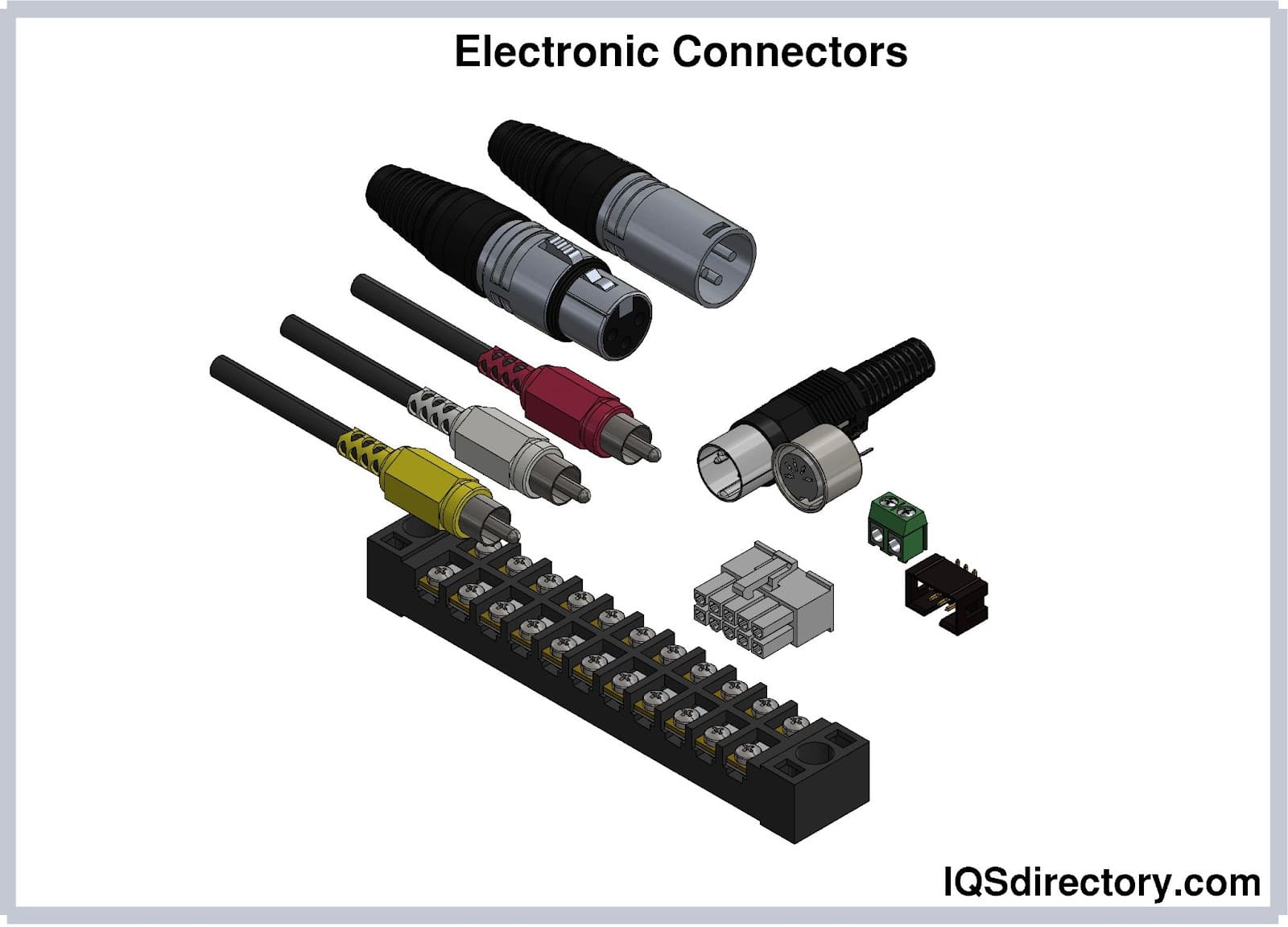
Devices that link electrical circuits are known as electrical connectors. While some connectors may be permanent, the majority are either temporary or detachable. Connectors allow for flexible design and modification options and enable circuit repairs. While some connectors may be permanent, the majority are either temporary or detachable. Read More…
Aries Electronics Inc. manufactures electronic interconnect products and other electronic components. Some products include zero insertion force test sockets, intelligent connectors, adapters, ball grid array sockets, land grid array sockets, high-frequency test sockets, and burn-in sockets.
Interpower is a company that is committed to providing industries with high-quality products. We manufacture electronic connectors. We make it easy for customers to design, build and maintain products for worldwide markets. We use teamwork to provide fast turnaround and great service to our customers.
Quail Electronics is a leading supplier of electrical components such as power cords and appliance electronic connectors. If you don't find what you need in our stock items, we can customize a product to meet needs.

Kord King manufactures world class electronic connectors, electric cords and plugs, electrical receptacles, plug adapters, cord sets and much more. From initial design to development, whether you are looking for a cable assembly or a power supply cord, the experienced team at Kord King delivers rapid order turn-around times and excellent products – consistently adhering to our strict quality...

More Electrical Connector Manufacturers
Electrical connectors are vital components in modern electronic systems, enabling flexible design, seamless modification, and efficient circuit repair. These essential devices are integral to communication, computing, industrial automation, and consumer electronics, serving as the critical interface between power sources, data signals, and electronic equipment.

What Is an Electrical Connector? Understanding the Basics
An electrical connector is an electromechanical device designed to join electrical circuits together. It allows for the rapid assembly, disassembly, or modification of circuits, which is crucial for maintenance and the scalability of electronic systems. Whether you are dealing with signal transmission, power distribution, or data communication, choosing the right connector ensures reliability, safety, and optimal performance.
Looking for guidance on how to select the best electrical connector for your application? Explore our detailed sections below for a comprehensive overview of connector types, components, and industry-specific considerations.
Electrical Connector Components: Anatomy & Purpose
Understanding the key components of electrical connectors is fundamental for making informed purchasing and engineering decisions. Every connector consists of:
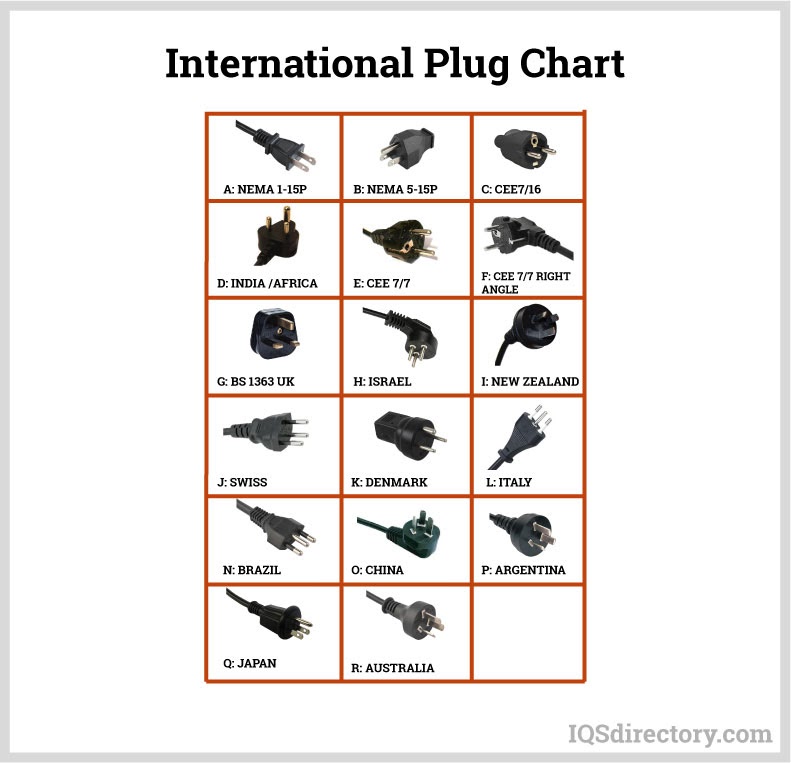
- Housing: The protective container or framework secures the connection, prevents short circuits, and guards contacts against environmental hazards such as dust, moisture, and temperature variations. Most housings are molded from high-strength plastics or engineered ceramics for excellent insulation and durability.
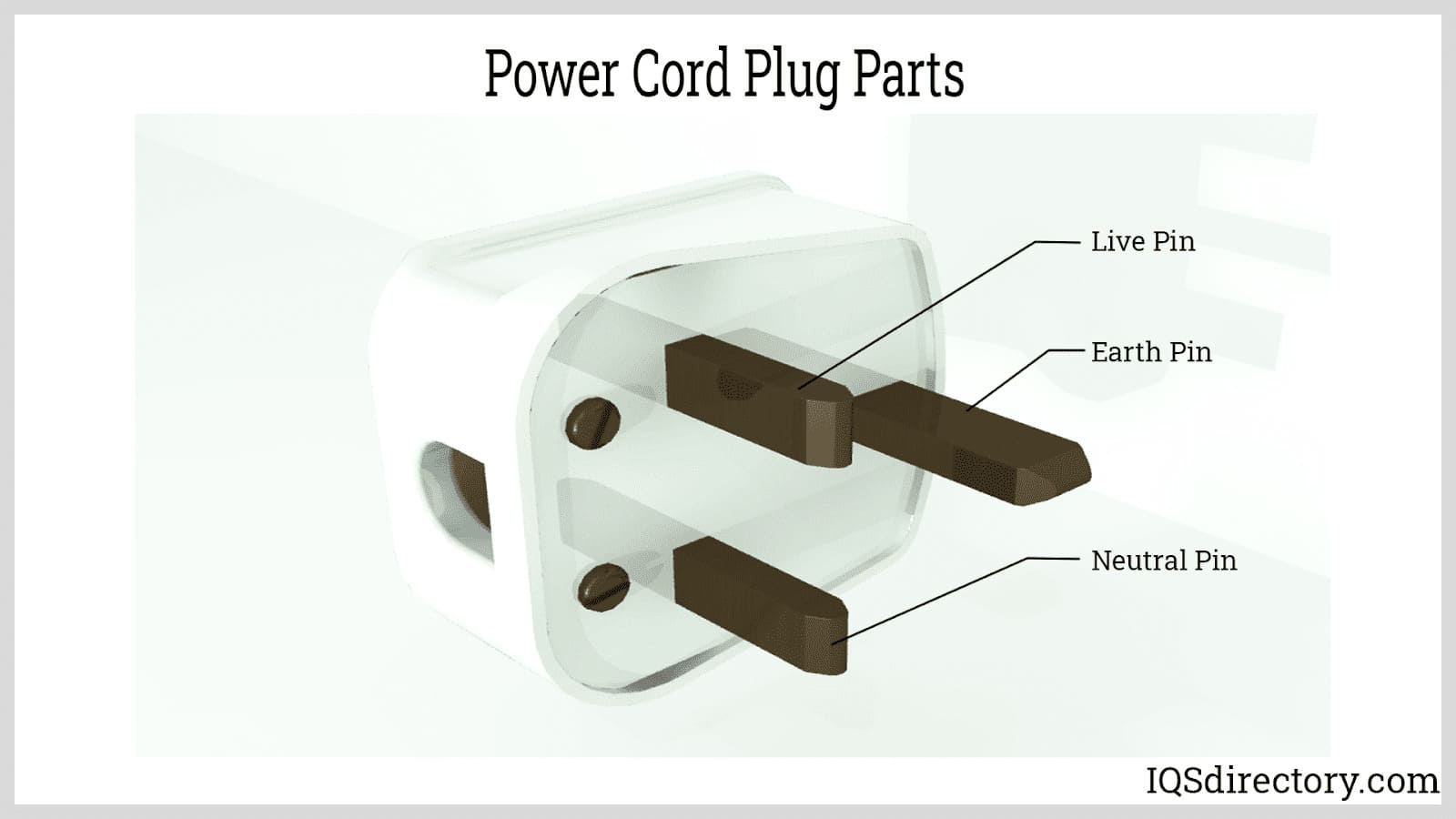
- Terminals (Contacts): These are the conductive elements—often pins, sockets, or blades—that establish the electrical pathway. Typically made of copper alloys, gold, or tin-plated metals, terminals ensure reliable conductivity and minimize resistance and signal loss. In some specialty connectors, materials like carbon or silicon are used to meet unique requirements.
Advanced connectors may also include features such as locking mechanisms, keying for correct alignment, environmental seals (IP-rated), and shielding to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Types of Electrical Connectors: A Complete Guide
Electrical connectors come in a vast array of forms tailored to specific uses, connection environments, and performance needs. Understanding the classification and application of these connectors can help you identify the most suitable type for your project or installation.
Connector Levels: How Are Electrical Connectors Classified?
In the electronics industry, connectors are often categorized based on their placement and function within a system. The National Electrical Distributors Association (NEDA) recognizes five primary connector levels:
- Wire-to-Board or Subassembly-to-Subassembly Level: Connects individual wires to printed circuit boards or subassemblies.
- Box-to-Box or Input/Output (I/O) Level: Enables connectivity between two separate enclosures or devices, often via cables.
- IC Chip or Chip-to-Package Level: Establishes electrical connections within integrated circuits or between chips and their packages.
- IC Package or Package-to-Board Level: Facilitates mounting and electrical connection of IC packages to circuit boards.
- PC Board-to-Board Level: Connects two or more printed circuit boards directly, allowing for modular design and expansion.
Understanding these levels is crucial for system designers, electrical engineers, and procurement specialists evaluating connectors for specific applications or compliance standards.
Connector Types by Function and Application
Let’s explore the most widely used electrical connector types, their unique features, and the industries or scenarios where each excels.
Audio and Video Connectors
Audio and video connectors enable the transmission of analog or digital signals between devices, while also providing necessary grounding and shielding. Common examples include RCA, XLR, 1/4" and 1/8" phone jacks, and HDMI connectors. These connectors are essential in professional audio-visual setups, home entertainment systems, recording studios, and broadcasting. Some models are designed to meet military specifications (Mil-Spec connectors), offering enhanced durability and signal integrity.

Automotive Electrical Connectors
Automotive connectors are engineered for reliability under high-vibration, temperature extremes, and exposure to moisture and chemicals. They are commonly found in engine management, infotainment, lighting, sensor modules, and powertrain systems. Popular types include blade connectors, weatherproof connectors, wire harness connectors, and OBD-II diagnostic connectors. Modern vehicles increasingly rely on these connectors for data communication (CAN, LIN) and power distribution.
Board Mount Connectors
Board mount connectors, or PCB connectors, are designed to be soldered or press-fit onto printed circuit boards. These connectors facilitate internal connections within electronic devices, supporting modular assembly and field serviceability. Applications include computer motherboards, industrial control panels, and medical devices. Types range from pin headers and sockets to edge card connectors and mezzanine connectors.
Board-to-Board Connectors
Board-to-board connectors establish connections between two or more circuit boards, supporting flexible configurations and compact device design. They are crucial in sectors such as telecommunications, aerospace, and consumer electronics. Options include stacking connectors, mezzanine connectors, and high-speed connectors for differential signal transmission.
Centronics Connectors
Centronics connectors are legacy parallel interface connectors, originally popularized by printers and peripheral devices. Characterized by two rows of flat contacts and a robust locking mechanism, they are still found in some industrial and legacy computing environments for data transfer and device control.
Circular Connectors
Circular connectors feature multi-pin designs within a round housing, offering robust mechanical protection and excellent EMI shielding. They are used in military, aerospace, industrial automation, and transportation sectors for transmitting power, control signals, and mixed data. Examples include MIL-DTL-5015, M12, and M23 connectors, each meeting various international standards for quality and safety.
Coaxial Connectors
Coaxial connectors provide shielded connections for RF (radio frequency) and high-speed data transmission. Built with a central conductor, dielectric insulator, and shielding, they are essential in television broadcasting, telecommunications, broadband networks, and instrumentation. Common types include BNC, F-type, SMA, and N-type connectors, each optimized for specific frequency ranges and impedance requirements.
DIN Connectors
Originating from the Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN) standards, DIN connectors are round, multi-pin connectors with precise keying and alignment features. They are widely used in audio equipment, MIDI interfaces, industrial controls, and legacy computing. Modern variants, such as mini-DIN connectors, serve as keyboard and mouse connectors in computers.

D-Subminiature Connectors
D-subminiature connectors (D-sub connectors) feature a D-shaped metal shield for mechanical durability and polarization. Available in various pin counts (e.g., DB9, DB25, DB37), these connectors are ubiquitous in computer serial ports, industrial automation, test equipment, and aerospace. Their design ensures secure mating, EMI protection, and reliable signal integrity.
Edge Connectors
Card edge connectors, also known as edge card connectors, create electrical connections with the exposed edge of a PCB (printed circuit board). Commonly used in memory modules (RAM), expansion cards (PCI, ISA), and modular hardware, these connectors facilitate rapid installation and replacement. Industry standards such as PICMG 1.0/1.2 define power requirements and pin layouts for system-level compatibility.
Fiber Channel Connectors
Fiber Channel connectors are high-speed, low-latency connectors designed for data storage networks, enterprise servers, and high-performance computing. They provide secure, lossless transmission over fiber optic cables. Typical types include LC, SC, and MTP/MPO connectors, supporting multi-gigabit data rates and hot-swappable configurations.
FireWire Connectors
FireWire connectors (IEEE 1394) support high-speed data, audio, and video transfer between digital devices. Used in professional video cameras, external drives, and multimedia equipment, FireWire’s daisy-chaining capabilities make it ideal for applications needing real-time data transfer with minimal latency. While USB has overtaken FireWire in many markets, legacy devices still rely on this robust connection standard.
Gender Changers
Gender changers are adapter devices that convert a connector’s gender, enabling compatibility between cables and equipment with identical or differing interface types. They are invaluable for field service, cable assembly, and rapid troubleshooting in IT, broadcast, and industrial environments.
Heavy Duty Rectangular Connectors
Heavy-duty rectangular connectors are designed for demanding industrial applications, delivering high power and direct signal connections in harsh environments. Featuring robust housings, secure locking mechanisms, and a variety of termination options (solder cups, wire wrap, crimp), these connectors are essential for control panels, robotics, factory automation, and energy distribution systems. They often meet rigorous standards for ingress protection (IP ratings), vibration resistance, and fire safety.
How to Choose the Right Electrical Connector: Key Considerations
With such a wide variety of connector types, selecting the optimal solution for your needs requires careful analysis of several factors. Here are the most important decision-making criteria when evaluating electrical connectors for purchase or engineering integration:
- Application Requirements: Identify whether the connector will carry power, transmit data, handle audio/video signals, or serve a mixed-use function.
- Electrical Ratings: Assess voltage, current, frequency, and signal type (analog or digital).
- Mechanical Durability: Consider mating cycles, insertion force, locking mechanisms, and environmental sealing (e.g., IP67, IP68 ratings).
- Environmental Conditions: Evaluate exposure to moisture, dust, chemicals, vibration, and temperature extremes.
- Size and Footprint: Ensure compatibility with available space and device form factor.
- Compliance & Certification: Check for industry-specific certifications (UL, RoHS, REACH, Mil-Spec, etc.).
- Installation & Maintenance: Review ease of assembly, field serviceability, and repair options.
- Cost & Availability: Balance quality, performance, and budget. Consider vendor reliability and lead times.
Frequently Asked Questions: Electrical Connectors
- What types of connectors are best for harsh environments?
Look for connectors with high IP ratings (IP67, IP68), ruggedized housings, and corrosion-resistant materials. Heavy-duty rectangular connectors, circular connectors, and certain automotive connectors are ideal. - How do I ensure signal integrity in high-speed data applications?
Select connectors with proper shielding, impedance matching, and low contact resistance. Coaxial and fiber channel connectors are commonly used for these purposes. - Which connectors are compatible with my PCB?
Board mount connectors, edge connectors, and board-to-board connectors are designed for direct PCB integration. Always check the footprint and pin layout before selection. - Can I use the same connector for power and data?
Some connectors (such as circular or hybrid connectors) are specifically designed to carry both power and control signals. Always confirm electrical ratings and isolation requirements. - How do I identify the gender of a connector?
Connectors are classified as male (pins) or female (sockets). Gender changers can adapt interfaces as needed. - Where can I find reputable electrical connector manufacturers?
Use our comprehensive manufacturer directory and RFQ tools to compare suppliers, view capabilities, and request quotes.
Industry Applications for Electrical Connectors
Electrical connectors are foundational across countless industries, each with its own performance standards and unique requirements. Some prominent application areas include:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, tablets, wearables, and home entertainment systems rely on compact, high-density connectors for data, charging, and audio/video interfaces.
- Automotive & Transportation: Modern vehicles, from passenger cars to electric vehicles (EVs) and heavy-duty trucks, depend on rugged connectors for powertrain systems, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment, and battery management.
- Industrial Automation: Programmable logic controllers (PLCs), robotics, and process control systems require secure, reliable connectors to ensure uptime and safety in factory and production environments.
- Aerospace & Defense: Mission-critical systems demand connectors with extreme vibration resistance, EMI shielding, and compliance with stringent military standards.
- Medical Devices: Diagnostic equipment, imaging systems, and patient monitors utilize precision connectors for low-noise signal transfer, sterilization compatibility, and small footprints.
- Telecommunications & Networking: High-frequency, high-density connectors power data centers, cellular base stations, and fiber optic networks.
- Renewable Energy: Solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems utilize weatherproof, high-current connectors for reliable power distribution and monitoring.
Benefits of Using High-Quality Electrical Connectors
Investing in the right connector technology yields significant advantages, including:
- Enhanced system reliability, reduced downtime, and easier maintenance
- Improved signal integrity and minimized data loss in high-speed applications
- Modular, scalable system design for rapid upgrades and repairs
- Compliance with safety and regulatory requirements
- Extended equipment lifespan and reduced total cost of ownership
- Customizable options for unique or demanding applications
How to Source Electrical Connectors: Tips for Buyers and Engineers
When sourcing electrical connectors, it’s essential to compare multiple suppliers and evaluate their capabilities. Consider the following steps for a successful procurement process:
- Define Your Requirements: List electrical, mechanical, and environmental needs for your connector.
- Research Connector Manufacturers: Use online directories, manufacturer websites, and industry forums to identify reputable brands and suppliers.
- Request Technical Documentation: Obtain datasheets, drawings, and compliance certificates to ensure compatibility and safety.
- Evaluate Samples and Prototypes: Test connectors in real-world conditions when possible to verify performance.
- Request Quotes and Compare Pricing: Use standardized RFQ (Request for Quote) forms to streamline the pricing and availability comparison process.
Ready to find the perfect connector? Visit our electrical connector manufacturer directory for detailed company profiles, website previews, and direct contact forms. Submit a single RFQ to connect with multiple trusted suppliers quickly and efficiently.
Choosing the Proper Electrical Connector Manufacturer: Why It Matters
Selecting the right manufacturer is crucial for product quality, supply chain reliability, and long-term support. Each electrical connector manufacturer featured in our directory has a dedicated business profile highlighting their specialties, certifications, and engineering expertise. Use our website previewer to explore their capabilities and our RFQ form to request custom quotes or additional information tailored to your project’s needs.
Related Resources & Further Reading
- Comprehensive Guide to Cable Connectors
- Industry Applications for Coaxial Connectors
- Electrical Connector Manufacturers Directory
- Wikipedia: Electrical Connectors
Explore More: Search-Driven Prompts
- What are the most common electrical connector types for industrial automation?
- How do I choose between circular and rectangular connectors for outdoor use?
- Which connectors are recommended for high-speed data transfer in telecom applications?
- Where can I buy RoHS-compliant electrical connectors in bulk?
- What is the difference between solder, crimp, and press-fit terminals?
- How do I troubleshoot faulty connections in PCB assemblies?
- Are there electrical connectors suitable for extreme temperature environments?
- How can I identify counterfeit or substandard connector products?
Still have questions about electrical connectors? Contact us today to connect with industry experts, request custom solutions, or get a detailed quote for your next project!









 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services